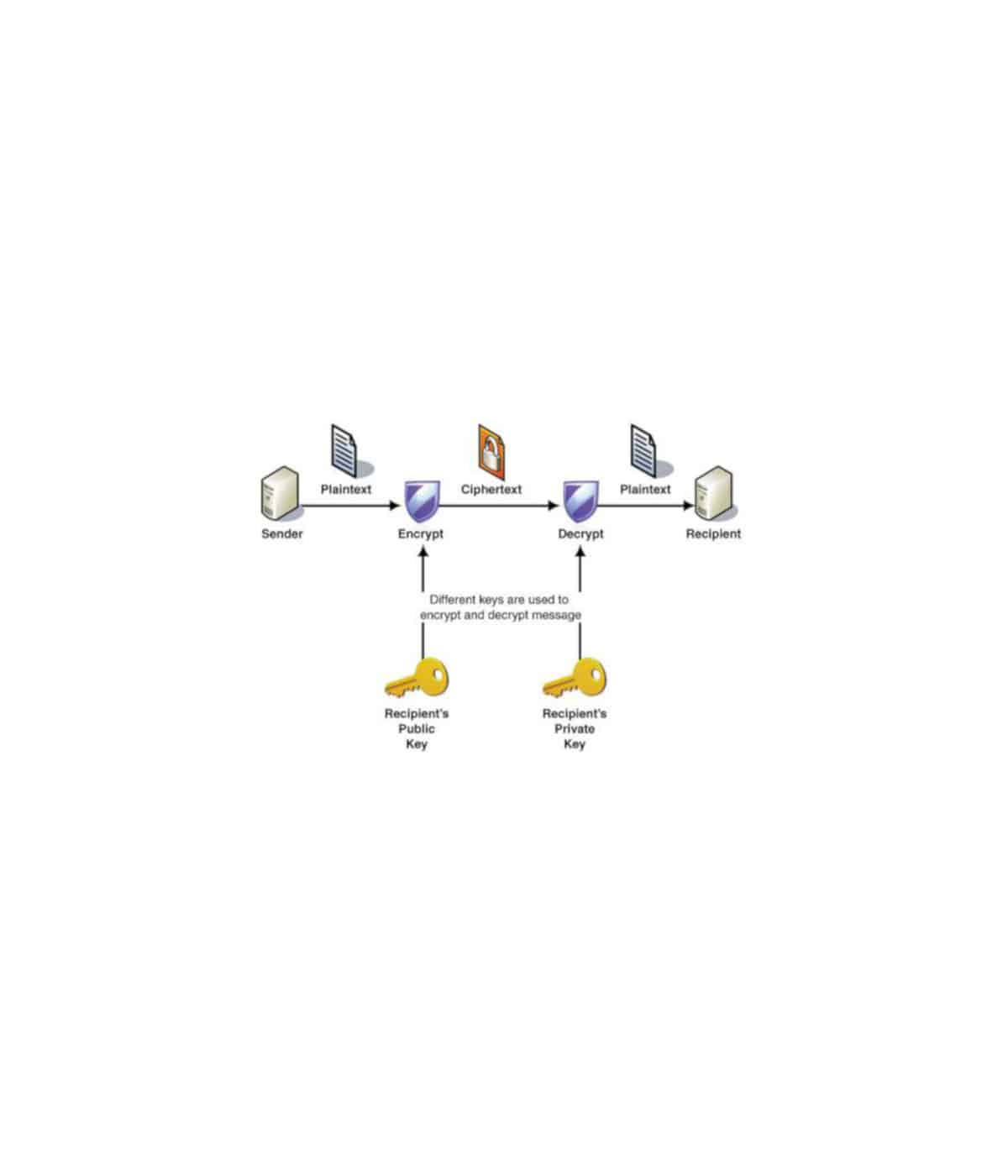
Name of the participant: Kailai Li
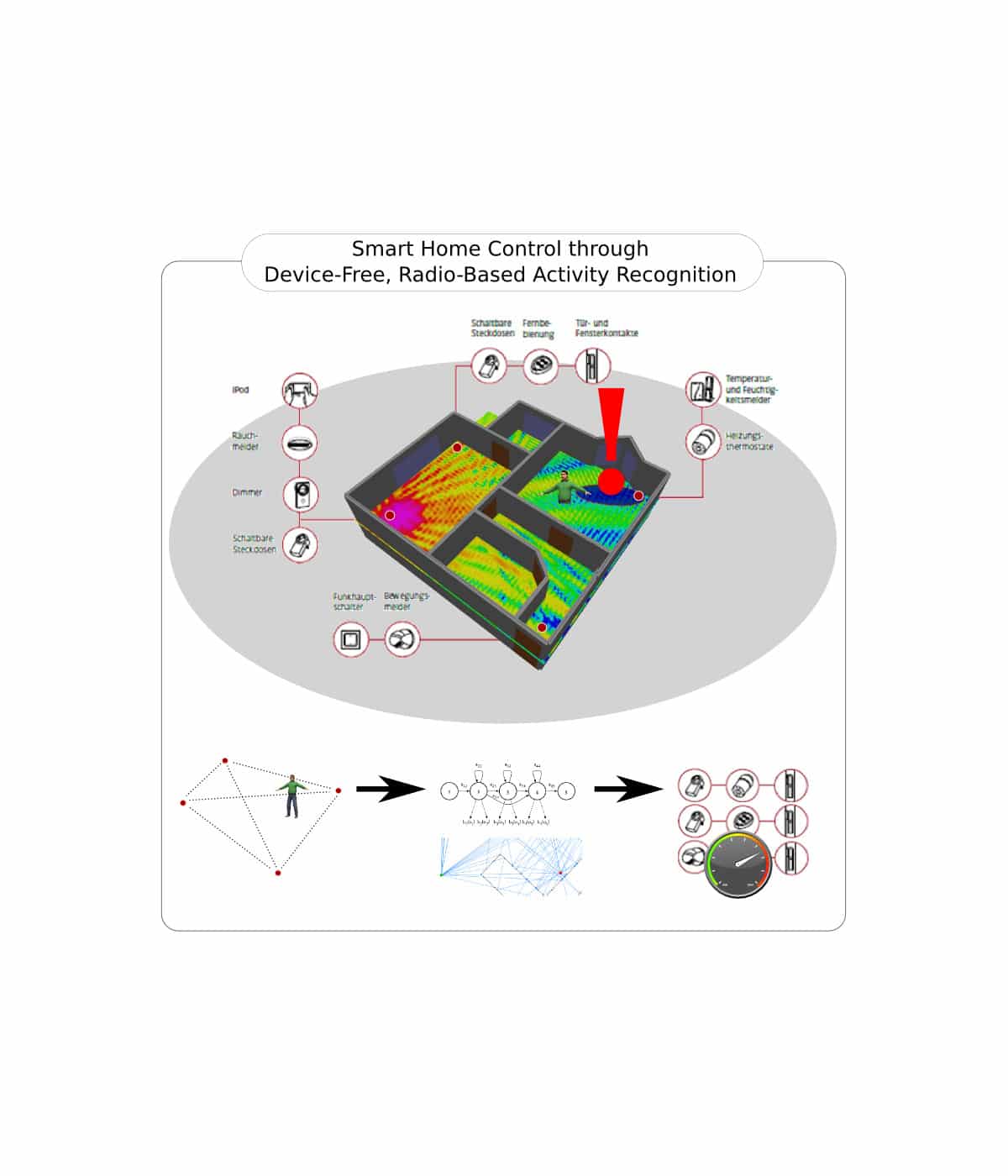
Description of the IT research project: Wireless sensor networks are used as infrastructure in various application scenarios such as autonomous driving, indoor localization and monitoring as well as robot navigation etc. In particular, the accurate and robust localization of mobile agents and mapping such as for shop floor monitoring play a central role in the context of intelligent factories and Industry 4.0. Due to advantages such as high data rate and precision as well as low power consumption, Ultra Wide Band (UWB) sensor networks are used in intelligent factories in extensive applications.
The aim of the project is to develop algorithms for object pose tracking and map generation using UWB-based sensor networks. The central application scenario here is production monitoring in intelligent factories where product components, machines and industrial trucks are to be tracked and the resulting dynamically changing map, which is to be reconstructed or updated in real time with adequate detail and accuracy. In order to achieve this goal, some aspects need to be given special attention. First, the current UWB inertial positioning technology of the industrial partner shall be upgraded to a 6-DoF pose tracking with improved accuracy and robustness. Within the pose tracker, an online calibration algorithm will be developed which allows for better scalability and reduces the effort for the use of UWB sensor networks in practice. Secondly, algorithms for the generation of a two-dimensional map of the dynamically changing production area are to be developed, based only on the trajectories of the tracked targets. Thirdly, sensors of other types, such as magnetic sensors, cameras or LiDAR, will be integrated as nodes in the existing UWB inertial sensor network. These heterogeneous networks are expected to have a beneficial effect on the performance of tracking and mapping.
Software Campus partner: KIT, Trumpf
Implementation period: 01.01.2020 – 31.05.2021